Posts Tagged ‘un’
IAPCAR Representative Addresses UN General Assembly First Committee
Wednesday, October 29th, 2014UN General Assembly
First Committee
October 28, 2014
[Downloadable PDF of First Committee SAF-IAPCAR Statement]
Statement of the Second Amendment Foundation
I am Julianne Versnel of the Second Amendment Foundation. I would like to address the topic of violence against women and the natural right of self-defense, especially as it pertains to women.
Mr. Chairman, more people die every day from malaria than are murdered by small arms in three days.1
More women and children die from starvation each day than are murdered by small arms in a 15 day period.2
More women die3 each day due to urgent medical care4 being denied them by systems that allow their male relatives to refuse care every day than are murdered by small arms.
More women are living in isolation because of societal ostracization caused by physical and mental disfigurements inflicted on them by men each year than are murdered with small arms. The acid burn victims in India,5 the 12 year old dehumanized brides,6 in Afghanistan, the women raped by armed-gangs in Mexico,7 and the mutilated, and do not forget murdered, victims of honor violence that occurs even in Europe, the Americas and Australia8 are just a few examples of these unspeakable crimes against women.
Gender violence9 often is perpetrated by male familial members of their families who do so with immunity and impunity–and in many instances with governments turning a blind eye,–condoning or even endorsing–the violence. To quote Amnesty International: “Perpetrators of violence against women are rarely held accountable for their acts. Women who are victims of gender-related violence often have little recourse because many state agencies are themselves guilty of gender bias and discriminatory practices. Violence against women is so deeply embedded in society that it often fails to garner public censure and outrage.”10
Mr. Chairman, the United Nations recognizes the right of governments to defend themselves, and to possess the means of doing so. Yet this body perpetuates the situation that keeps the number of women victims growing by denying them, and in fact all human beings, the means to–and decrying even their right to—defend themselves. They are the victims not of small arms, but of political philosophies and state policies that say only governments are worthy of defending themselves. To argue that people have the right to live but not to defend their lives is to argue in favor of continuing to keep women at risk of criminal violence in places where government does little to protect them.
Mr. Chairman, this body must address the right of women to defend themselves and their right to have the physical means–including firearms—of doing so. Or, acknowledge the hypocrisy inherent in proclaiming support for women’s causes while keeping them vulnerable to male-perpetuated criminal violence.11
Thank you.
Endnotes
1. According to UNODC statistics there are 538 homicides worldwide each day. See http://www.unodc.org/documents/data-and-analysis/statistics/Homicide/Globa_study_on_homicide_2011_web.pdf. There are an estimated 1718 deaths from malaria every day. See http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/malaria/en/ According to UN estimates there will be almost 10,000 cases per week of Ebola. With an anticipated 70% mortality rate, there would be 1000 deaths per day from this disease.
2. According to http://www.wfp.org/hunger/stats, 8493 children die each day from hunger.
3. 315 thousand women die in developing countries from hemorrhage at childbirth each year, 863 each day. See http://www.wfp.org/hunger/who-are.This does not include death from disease and other causes where a male family member will not allow a female family member to receive medical care. For example, in some parts of Africa, a midwife cannot even be called to help with a birth without male permission.
4. There are an estimate 2-4 million women with an obstetric fistula in Africa. There are between 50 and 100 thousand more cases per year. This serious medical condition is caused by a lack of essential medical care. See http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/obstetric_fistula/en/
5. There are an estimated one thousand acid attacks each year. See http://techcrunch.com/2013/08/02/acid-victims-crowdfund-treatment/.
6. One in four girls globally are child brides; they are married before the age of 15. These girls are more likely to have a large number of children, a low level of education, and less likely to receive medical care during pregnancy. See http://data.unicef.org/corecode/uploads/document6/uploaded_pdfs/corecode/Child-Marriage-Brochure-7_17-HR_164.pdf)
7. See http://www.ipsnews.net/2014/06/mexico-rape-victims-face-prison-time-for-self-defence/ and http://globalvoicesonline.org/2013/11/26/machismo-and-old-prejudices-keep-mexican-rape-victims-silent/
8. See http://www.meforum.org/2646/worldwide-trends-in-honor-killings. In 2000, the UN estimated that there were approximately 5000 honor murders per year. This figure only includes killings, not mutilation. See http://nypost.com/2014/06/26/honor-killings-daughter-worked-with-feds-to-catch-father-making-threats/, http://www.mapsofworld.com/poll/is-honor-killing-honorable-facts-infographic-text.html
9. “There is one universal truth, applicable to all countries, cultures and communities: violence against women is never acceptable, never excusable, never tolerable.”
United Nations Secretary-General, Ban Ki-Moon (2008)
10. See http://www.amnestyusa.org/our-work/issues/women-s-rights/violence-against-women/violence-against-women-information for complete quote.
11. Additionally:
• Women are by natural usually pacifists. They are the first to agree to non-violence policies and the first to be victimized by those policies.
• Women are statistically going to be victimized.
• The current policies have created and institutionalized a policy of violence against women.
• There is a cultural norm that allows women to expect safety in public but not in private, and increasingly not even in public.
• Violence against women is female reality. Over the past eight years, at least 40,000 women were killed in India alone in dowry deaths despite several new legislative actions in recent years.
• The lack of access to small arms does not stop violence against women. Rather it enables its escalation as perpetrators know that their victims are unable to defend themselves.
• The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, The Declaration on the Elimination of Violence Against Women and the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) are violated by not allowing women a means to self-defense.
• There are numerous other reasons for and causes of femicide: gender selection abortions, female genital mutilation, human trafficking, murder of female babies at birth, etc. that are not addressed.
• It is estimated that 35.6% percent of women globally have experienced physical or sexual violence during their lifetimes. This is more than 1.2 billion women. As the 2011 Global Study on Homicide shows, gender-based violence affects a large number of women worldwide and represents a serious threat to the harmonious development of societies.
Gun Trade World Article: Arms Trade Treaty Under Scrutiny
Monday, November 11th, 2013Feature story in November 2013 print edition of Gun Trade World.
Available online linked here.
US State Dept. Press Release: “US Welcomes Opening of Arms Trade Treaty for Signature”
Monday, June 3rd, 2013Press Statement
Secretary of State
The United States welcomes the opening of the Arms Trade Treaty for signature, and we look forward to signing it as soon as the process of conforming the official translations is completed satisfactorily.
The Treaty is an important contribution to efforts to stem the illicit trade in conventional weapons, which fuels conflict, empowers violent extremists, and contributes to violations of human rights. The Treaty will require the parties to implement strict controls, of the kind the United States already has in place, on the international transfer of conventional arms to prevent their diversion and misuse and create greater international cooperation against black market arms merchants. The ATT will not undermine the legitimate international trade in conventional weapons, interfere with national sovereignty, or infringe on the rights of American citizens, including our Second Amendment rights.
We commend the Presidents of the two UN negotiating conferences – Roberto Garcia Moritan of Argentina and Peter Woolcott of Australia –for their leadership in bringing this agreement to fruition. We also congratulate all the states that helped achieve an effective, implementable Treaty that will reduce the risk that international transfers of conventional arms will be used to carry out the world’s worst crimes.
The Real Truth About Gun Homicides
Monday, May 20th, 2013The UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) global map of homicide rate shows lower rates in countries with higher gun ownership.
NSSF Objects to U.S. Government Abandoning Position that U.N. Treaty Must be based on International “Consensus”
Monday, April 1st, 2013Via: National Shooting Sports Foundation (NSSF)
The National Shooting Sports Foundation today strongly objected to the last-minute reversal of the U.S. government position regarding the United Nations Arms Trade Treaty. In the closing hours of negotiations on Thursday, March 28, the government abandoned its previous insistence that the treaty be approved only through achieving “consensus” of all the member states. Requiring consensus had been the United States position going back to earlier administrations.
At the end of the session, a U.S. government spokesperson told reporters “It’s important to the United States and the defense of our interests to insist on consensus. But every state in this process has always been conscious of the fact that if consensus is not reached in this process, that there are other ways to adopt this treaty, including via a vote of the General Assembly.” The spokesperson went on to say that the United States would vote “yes” on the treaty in the General Assembly, regardless of the positions of other member states. By abandoning the requirement for consensus the United States is assuring passage of the treaty by the United Nations.
“This abrupt about-face on the long-standing United States requirement for ‘consensus’ illustrates that the Obama Administration wants a sweeping U.N. arms control treaty,” said Lawrence Keane, NSSF senior vice president and general counsel. “We are troubled by the timing of the Obama Administration’s decision to abandon consensus on the eve of the Senate debate on pending gun control measures. The United Nations treaty would have a broad impact on the U.S. firearms industry and its base of consumers in the U.S.”
Industry analysts have identified three major areas of concern with the treaty text. The treaty clearly covers trade in civilian firearms, not just military arms and equipment. It will have a major impact on the importation of firearms to the United States, which is a substantial source for the consumer market. And it will impose new regulations on the “transit” of firearms, the term defined so broadly that it would cover all everything from container ships stopping at ports to individuals who are traveling internationally with a single firearm for hunting or other sporting purposes.
“We hope that the Members of the U.S. Senate are closely watching the White House abandon its principles and promises in the rush to ramrod this flawed treaty into effect. Not only will they later be asked to ratify this attack on our constitution and sovereignty, but they will also be lavished with new promises from the administration in its drive to push a broad gun control agenda through the U.S. Senate when it returns from recess. They would be right to question those promises strongly,” concluded Keane.
Arms Trade Treaty Discussed at UN, Second ATT Conference Scheduled for 2013
Friday, November 16th, 2012Original Story Via: TheGunMag.com
New York, NY—The UN Arms Trade Treaty (ATT) was discussed at length with testimony from both pro and anti-gun groups during the First Committee of the United Nations General Assembly’s 67th session.
On Nov. 7, a resolution was passed for a second ATT conference beginning March 18. The UN already spent 11 weeks in meetings for the ATT with four Preparatory Committee meetings leading toward the final failed ATT conference last July. The General Assembly will consider the resolution; it’s likely that it will be approved.
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGO’s) were scheduled for Oct. 29; however, the UN was closed due to Hurricane Sandy. Statements for all NGOs were delivered in written form to the delegates. The NGO statements to the UN against guns were juxtaposed against looting in the wake of Hurricane Sandy, with many local New York and New Jersey citizens unable to protect themselves due to some of the most strict gun laws in the country. TheGunMag.com (TGM) outlined the tragic irony of the situation here: SAF: Post-Storm Brooklyn Looting Shows Importance of Gun Rights.
The Second Amendment Foundation delivered its remarks to the UN with other groups as detailed in a previous TGM stories here: SAF, others weigh in on new round of UN gun control talks, and SAF Statement to UN Stopped by Storm, Still Carries Powerful Message. SAF also addressed the UN’s Programme of Action in August defending the human right of self-defense.
At the first committee meetings, the right to keep and bear arms in self-defense was not discussed. Canada reaffirmed the right of its citizens to own and use firearms for sporting purposes. The delegates focused primarily on consensus, negotiation, and implementation. The case was made for expansion of the scope and parameters of the ATT document from July 2012. Of particular note were points made about registration, tracing, and tracking of guns and ammunition. An official version of the meeting is available here.
The draft ATT in July didn’t win any acclaim from any Second Amendment or self-defense rights groups. That’s not stopping NGO’s like Control Arms from claiming the July draft of the ATT was “missing pieces.”
The following are statements from the Defense Small Arms Advisory Council (DSAAC), the World Forum on Shooting Activities (WFSA), the Sporting Arms and Ammunition Manufacturers’ Institute (SAAMI), the Manufacturers Advisory Group to the World Forum on Shooting Activities, and the International Committee of Museums and Collections of Arms and Military History.
TheGunMag and IAPCAR were among the first to make the July 24 initial draft and final UN ATT proposal publicly available. More information about the ATT will be reported as it becomes available on TheGunMag.com, SAF.org, and IAPCAR.org.
Statement of the Defense Small Arms Advisory Council
First Committee of the United Nations General Assembly
29 October 2012
Thank you, Mister President, for the opportunity to offer remarks from the perspective of an industry that manufactures military small arms and light weapons to enable states to meet their legitimate national security and law enforcement requirements and does so in strict compliance with the most demanding and rigorous export licensing system in the world. We believe that a legally binding Arms Trade Treaty that subjects all military arms manufacturers and exporters world-wide to a similar level of regulation can be of benefit in combating the armed violence caused by the absence of common standards governing the international trade in military weapons. It is difficult to ignore the fact that the vast majority of states currently lack even the most rudimentary export licensing systems, much less comprehensive ones with correspondingly effective enforcement mechanisms. The ATT was, we thought, to begin addressing that lack.
From our perspective as observers of the negotiations conference in July, it appears that the chief obstacle to achieving consensus on an effective treaty text was the insistence by some on creating an overly broad document, one that went well beyond the committee’s mandate, irrespective of the fact that such language was unlikely to ever be agreed and, even if agreed, effectively carried into force. A treaty can be likened to a vessel: it can carry only so much freight and attempting to overload it with too many things that, although desirable to some are objectionable to others, poses the risk of sinking it. In July, the vessel was overloaded and nearly sank; fortunately, it was still tied to the pier and may yet set sail, once the excess weight is removed.
It is our understanding that the sole purpose of the ATT is to legally compel state-parties to adopt procedures for determining if a proposed export of military arms meets basic, internationally agreed standards. Treaty language that is narrowly focused on achieving that single purpose is, we believe, well worth working for and still well within reach. It is to be hoped that future negotiations retain that focus and that the perfect—in the eyes of some—does not once again become the enemy of the good.
###
Statement From: Manufacturers Advisory Group
Ted Rowe, Chairman
Mr. Chairman:
I am Ted Rowe, Chairman of the Manufacturers Advisory Group to the World Forum on Shooting Activities (WFSA). Speaking on behalf of the world’s leading manufacturers of civilian firearms and ammunition, we must insist on the recognition of civilian possession and ownership of firearms and ammunition in accordance with national law.
Unless and until the United Nations in its various proposals recognizes the right of lawful civilian ownership and possession of firearms, we will continue to use all efforts necessary to have civilian ownership recognized by the United Nations, and we will continue to oppose those proposals that do not recognize this right.
The Arms Trade Treaty to be negotiated in March of 2013 should clearly indicate that the small arms included are for military use and that civilian firearms are to be excluded.
The Program of Action as it evolves should also recognize the legitimate, legal use of firearms by civilians as well as their right to own and possess firearms within their national laws.
It is interesting to note that each and every member state of the United Nations is a legitimate importer of civilian firearms and ammunition. These imports are not for the military! These imports should not be subject to or included within an Arms Trade Treaty.
Civilian use of firearms is seen internationally in Olympic Games, in hunting around the world, in sport shooting and in recreational use.
Finally, Mr. Chairman, there is the human right of self-protection and self-defense and the need and use of firearms to fulfill that right. This right is indisputable and is documented throughout history.
Thank you, Mr. Chairman
###
Statement from World Forum on Shooting Activities (WFSA)
UN General Assembly First Committee
October 29, 2012
Mr. Chairman, I am Herbert Keusgen, the President of the World Forum on Shooting Activities. We represent the hundreds of millions of hunters, sport shooters and civilian firearms owners throughout the world. The WFSA is an ECOSOC NGO and has participated in UN meetings relating to small arms and light weapons for fifteen years.
Today I would like to make three brief comments, reflecting the views the civilian firearms community, on the Programme of Action, the possible Arms Trade Treaty and ISACS.
On the Programme of Action, Mr. Chairman, we continue to remain disappointed that the POA has failed to recognize the legitimacy and utility of civilian firearms ownership. Mr. Chairman, there seems to be a continuing misconception on the part of the UN and supporters of the POA, that civilian firearms are a bad thing. Sixty percent of the small arms in the world are legally owned by civilians. These arms are not a problem. The problem lies with inadequate control of military arms.
Mr. Chairman, let’s say something positive. At the last week’s UN meeting on the UN Firearms Protocol in Vienna there was an acknowledgment of the legitimacy of civilian firearms use. This was a positive step and we commend this action.
Mr. Chairman, in regard to a possible Arms Trade Treaty, we continue to be told that the intent of an ATT is only to control military small arms. Therefore, we request the UN to state this in such an ATT in clear and unmistakable language. For example, it could use the definition of SALW used by Germany, and I quote:
Small Arms and Light Weapons (SALW), are weapons and weapon systems which were originally manufactured or which were rebuilt according to military standards and requirements for use as war matériel.
This would clearly exclude civilian firearms from the scope of the ATT.
Mr. Chairman, the ATT has been extremely politicized in one particular jurisdiction. This is a question of perception, Mr. Chairman. As long as the ATT is perceived, let me underline perceived, as affecting civilian firearms, it will not be accepted or ratified in that jurisdiction. This situation can be changed by the specific exclusion of civilian firearms that we have suggested.
Mr. Chairman, let me briefly comment on International Small Arms Control Standards or ISACS. We are extremely disappointed in the ISACS process. If the POA has had a bias against civilian firearms, ISACS has been almost overtly anti-civilian firearms. The ISACS process has failed to respond appropriately to the legitimate concerns and requirements of the civilian user community and the firearms manufacturers. This must change, Mr. Chairman.
Let me conclude, Mr. Chairman, by saying that notwithstanding our criticisms today we remain willing to cooperate on all fronts and venues whether it be the POA, the Firearms Protocol, the ATT or ISACS. We can be a valuable ally to efforts that address the problems of misuse or a steadfast opponent of any effort that restrict the lawful use of civilian firearms.
For further information contact Thomas Mason at +1 503 998 0555 or tlmorusa@aol.com .
###
United Nations General Assembly, 67th Session
First Committee
New York, 1 November, 2012
Statement by Richard Patterson, Managing Director
Sporting Arms and Ammunition Manufacturers’ Institute, Inc
Thank you, Mr. President, for the opportunity to speak today. My name is Richard Patterson. I’m the managing director of the Sporting Arms and Ammunition Manufacturers’ Institute–also known as SAAMI. Since 1926 we have created the safety and reliability standards for the design, manufacture, transportation, storage and use of firearms, ammunition and components. We are an accredited standards-setting organization. Whether you realize it or not, every country in this room benefits from our standards. Firearms and ammunition that follow SAAMI standards are being used in every corner of the world to promote peace, enhance economic stability, responsibly manage wildlife populations, provide recreation, teach life-skills, promote the camaraderie of sporting competition, and protect lives.
The small arms issue is complex, since small arms are tools that can be used for the greater good of humanity, and misused by those who choose to commit acts of violence. Because of this duality, uninformed decisions can cause more harm than good.
SAAMI has at its disposal many of the world’s leading ballisticians, structural engineers, chemists, statisticians, logistics experts, and metallurgists specializing in firearms and ammunition. We are in the unique position of providing valuable technical, factual, and science-based input into the small arms discussion and debate. We also have access to the real-world practical knowledge of the major manufacturers of firearms, ammunition and components, meaning we can add a practical perspective to the debate.
We welcome the opportunity to share our expertise and experience. We would like to participate in any discussions resulting from the PoA call for a technical and industry working group and—for that matter—in any other discussions on this important issue.
###
Statement From: The International Committee of Museums and Collections of Arms and Military History (ICOMAM)
2012/10/24
Mr. Chairman:
I am Ken Smith-Christmas, representing ICOMAM, The International Committee of Museums and Collections of Arms and Military History. ICOMAM is an organization with approximately 260 institutional and individual members in some 50 countries, and includes such museums as the Royal Armouries in England, the Royal Dutch Army Museum, the Royal Belgian Army Museum, and the Smithsonian Institution. For the past fifty-five years, we have served as the advocate for museums around the world that specialize in arms and military history. We are an international committee of ICOM, the International Council of Museums, which works closely with UNESCO.
Nearly every history museum on earth has firearms in its collections. Most of these arms are antique, or, by their historical association, are considered to be curios. Many of them are inoperable relics, due to their physical condition. Some are excavated, archaeological, material. The ability to acquire and exchange them is essential to the scientific, cultural, and economic functioning of our museums. We are concerned that the provisions of the Arms Trade Treaty will affect these types of firearms. For instance, under proposals currently being reviewed, a museum would have to seek the permission of the exporting country, the importing country, and the transit countries to acquire and transport an antique arm or weapon, even for a temporary loan or a research project.
We submit that antique arms and museum weapons pose no threat to anyone. Rather, they are part of our common cultural heritage and current regulatory structures are adequate to control them. Additionally, in today’s climate of constrained budgets, it is an unnecessary financial burden on museums and governments to require stringent controls over the antiques, curios, and relic arms commonly found in museums.
In short, we believe that there is simply no need for antique and museum arms and weapons to be included within the scope of an Arms Trade Treaty. We therefore request that they be exempted from the scope of any Treaty.
Thank you.
Canada: Conservatives defy UN gun controls
Monday, November 5th, 2012By Mark Dunn, Senior National Reporter
Rifle enthusiasts celebrating the destruction of most long-gun registry files last week have more to cheer about after the government again deferred a plan gun-control advocates say would combat illegal arms trafficking.
Opponents argue the United Nations protocol signed by a previous Liberal government would drive up the cost of guns by as much as $200 apiece, killing jobs and creating more red tape in an already overregulated industry.
Proponents argue ignoring the framework is a step backwards to trace traffickers of guns to civil wars and Third World conflicts – some of which end up in the hands of local criminals.
The protocol – on hold until December 2013 – would require all imported guns to be marked with the name of the country and year of import. It’s at least the fourth time the government has punted the regulation since taking office in 2006.
QMI Agency learned of the latest postponement after obtaining a briefing note to Conservative MPs from Public Safety Minister Vic Toews dated Nov. 2.
Toews said he is listening to sports-gun owners, retailers, distributors and importers who say the cost to engrave importation markings on new firearms would come after the manufacturing process and be passed down to buyers.
|
|
“We have heard the concerns and will not be moving forward until consultations have occurred,” caucus was told.
The Canadian National Firearms Association (NFA) welcomed the delay.
“There was significant concern in from both firearms businesses and members of the firearms community as well as many MPs about the need to go forward with a regulatory scheme brought in by a previous government when that scheme would add significant cost to products and damage the economy of an already over-regulated business,” said NFA president Sheldon Clare.
A spokesperson for the Coalition For Gun Control wouldn’t comment, but on its website the anti-gun lobby suggests the government has no intention of ever complying.
“After eliminating registration and records of sales, Canada has now eliminated yet another tracing mechanism for firearms and appears to have given up completely complying with the UN Firearms Protocol and with providing police with effective ways to trace guns found in crime and fight illegal gun trafficking.”
How the 2012 UN Arms Trade Treaty Conference Really Died
Thursday, October 18th, 2012(H/T Jeff Moran, TSM Worldwide)
By Jeff Moran | Geneva
Advocacy and diplomatic discussions started again last week with the opening day of the UN General Assembly First Committee meetings.[1] These meetings end on 6 November 2012 (Election Day in the United States), and follow-up the failed United Nations (UN) Conference in July to formally negotiate by consensus a legally binding Arms Trade Treaty (ATT).[2]
Contrary to prevailing reportage and opinion, the UN ATT Conference was less a failure in diplomacy, or a victory by the firearms industry and the National Rifle Association for that matter, than it was the result of abortive advocacy lead by the UK-based Control Arms campaign and its unrealistically expansive vision for a more extreme trade treaty than consensus could sustain.[3]
The Control Arms vision for the ATT encompasses 14 specific treaty issue areas under three categories: Scope, Transfer Criteria, and Implementation. Scope issues areas include Ammunition, Brokering/Dealers, Other Conventional Weapons, and Small Arms/Light Weapons. Transfer Criteria issue areas include Armed Violence, Corruption, Gender-based Violence, Human Rights, International Humanitarian Law, and Socio-Economic Development. Implementation issue areas include Final Provisions, Implementation, Verification, and Victim Assistance.
The Control Arms vision across these treaty issue areas can be found on their subsidiary armstreaty.org website.[4] The details of their ATT vision are quoted below:
1. Ammunition. Including in the scope of the ATT all “ammunition, munitions, and explosives.”
2. Brokering/Dealers. Including in the scope of the ATT brokering and dealing. “Brokering generally refers to arranging or mediating arms deals and buying or selling arms on one’s own account or for others, as well as organizing services such as transportation, insurance or financing related to arms transfers, and the actual provision of such services.”
3. Other Conventional Weapons. Including in the scope of the ATT “all conventional weapons, related components and production equipment, beyond Small Arms and Ammunition” which are “covered by the 7 categories in UN Register of Conventional Arms and of other conventional weapons, components and equipment.”
4. Small Arms/Light Weapons. Including in the scope of the ATT “conventional weapons that can be carried by an individual or a group of individuals (including revolvers, machine guns, hand-held grenade launchers; portable anti-aircraft and anti-tank guns and missile systems; and mortars of calibers less than 100 mm. etc).”
5. Armed Violence. Including as a parameter of the ATT “provisions to restrict transfers that could provoke, fuel or exacerbate armed conflict and armed violence.”
6. Corruption. Including as a parameter of the ATT “provisions to restrict transfers that could exacerbate or institutionalize ‘corruption’ or ‘corrupt practices’. In the context of arms transfers, corrupt practices include bribing of state officials with commissions and kickbacks provided by arms producers and traders to facilitate a transfer agreement.”
7. Gender-based Violence. Including as a parameter of the ATT provisions to “restrict the transfer of arms where there is a substantial risk that the arms under consideration will be used to perpetuate or facilitate acts of gender-based violence, including sexual violence.”
8. Human Rights. Including as a parameter of the ATT “provisions to restrict transfers when there is substantial risk that the arms will be used in serious violations of international human rights law, including fueling persistent, grave or systematic violations or patterns of abuse.”
9. International Humanitarian Law. Including as a parameter of the ATT “provisions to restrict transfers when there is substantial risk of the arms being used in serious violations of international humanitarian law (IHL). This assessment would include consideration of whether a recipient that is, or has been, engaged in an armed conflict has committed serious violations of IHL or has taken measures to prevent violations of IHL, including punishing those responsible.”
10. Socio-Economic Development. Including as a parameter of the ATT “provisions to restrict transfers that could hinder, undermine or adversely affect socio-economic development.”
11. Final Provisions. Including in the text of the ATT “effective implementation mechanisms of the Arms Trade Treaty, including criminalization of treaty violations and an Implementation Support Unit (ISU) to coordinate international cooperation.”
12. Implementation. Including in the text of the ATT final provisions and entry into force mechanisms. “Effective final provisions would not allow reservations that would be incompatible with the Treaty’s purpose. Effective entry into force mechanisms would not include a requirement for excessive number of ratifications, nor for specific states or groups of states to ratify the treaty, before it could enter into force.”
13. Verification. Including in the text of the ATT “effective verification mechanisms of the Arms Trade Treaty. Effective verification includes meaningful and specific annual reporting, external referral for dispute resolution, annual meetings of states party (MSP) and five-yearly Treaty Review Conferences (RevCons), and the creation of an Implementation Support Unit (ISU) to assist with, collect and analyze reports.”
14. Victim Assistance. Including in the text of the ATT “the recognition of the rights of victims of armed violence and acknowledgment of States’ commitment to provide assistance to victims.”
Reaching consensus during the UN ATT Conference was certainly possible, and potentially a constructive endeavor for all nations from an interest point of view. But consensus was not likely because a lot of countries thought aspects of the emerging ATT were potentially threatening to national sovereignty for example.[5] Nonetheless, the popular narrative is that the United States killed the Conference when it asked for more time to consider the draft treaty on the final day of the Conference.[6] This expedient and seemingly anti-American explanation doesn’t stand up to scrutiny, especially when you put the Conference into context and examine the armstreaty.org database about opposition to the ATT.
The relevant historical context for what happened at the Conference extends back to at least the creation of the International Action Network On Small Arms (IANSA) in 1999. Important context also includes the recorded debate between the leaders of IANSA and the National Rifle Association in 2004 along with several formal rounds of preparatory negotiations since 2009 for example. This is admittedly a lot of history for one to casually consider, but after surveying this period, and listening to diplomats based in Geneva, a pattern of overdone, unfocussed, and ultimately counterproductive advocacy emerges. This appears to be due, at least in part, to self-inflicted wounds from years of overselling positions and distractive issue framing, which, in turn, appears to have damaged their credibility and cause.[7] Ultimately, humanitarian groups, led by an unraveling Control Arms coalition, sabotaged consensus for an ATT by pushing diplomats too hard for far too much and provoked dispositive sovereignty concerns across the Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East in addition to the United States.[8]
Not only was there no consensus on the final draft ATT as a whole in those final days of the Conference, but there remains no consensus for any of the 14 treaty elements Control Arms continues to advocate for, and opposition to them is growing. This can be evidenced in detail on armstreaty.org.[9] While the data on armstreaty.org are not an official record of country delegation viewpoints during the final days of the ATT conference, they serve as a useful proxy indicating size, scope, and direction of opposition to the ATT as Control Arms envisions it.
Clearly, the most widely opposed ATT issue areas fall under the creation of transfer conditionality / restrictive criteria on the international transfers of arms. The most objected-to transfer criteria remain those related to Socio-Economic Development and Human Rights. Thirty-nine and 35 countries oppose these criteria respectively, the US not being among them. The US opposed only three provisions cutting across treaty scope and implementation issue areas only.[10]
The accompanying table below is made from armstreaty.org data and evidences the above points. It also conveys more important details about the lack of consensus for an ATT. The table indicates, from a treaty content point of view, where opposition is greatest, the relative size of the opposition, and the direction of opposition since the Conference. [11]
In short, the table below helps show why the assertion that the US is mainly responsible for killing consensus at the UN ATT Conference is not only false, but absurd. Here are nine take-aways:
1. There are 195 total instances where a country opposes an aspect of the envisioned ATT (consensus requires zero instances or at least a willingness to no longer publicly oppose, and Control Arms attributes just 3 of these 195 to the US).
2. There is no consensus for any of the provisions across the all three treaty issue area categories (Scope, Transfer Criteria, and Implementation).
3. Total opposition to the Control Arms vision has actually grown in the months after the UN ATT Conference (by 12 net instances, or 7%).
4. There is a two-way tie for issue areas experiencing the fastest opposition growth: Socio- Economic Development and International Humanitarian Law (both together account for 2/3 of the growth in total opposition).
5. The most-opposed category of treaty issue area is Transfer Criteria (54% share of total opposition) and opposition has grown (by 11 instances, or 6%, since 29 August 2012).
6. The most-opposed treaty issue area by country count is Socio-Economic Development (39 countries opposed).
7. The most-opposed issue area by percentage of countries opposed (relative to total number of countries assessed) is Human Rights (33%).
8. The least-opposed provision by country count relates to including the activities of arms Brokering/Dealing within the scope of the ATT (2 countries opposed).
9. There is a three-way tie for the least opposed provisions by percentage of countries opposed (relative to total number of countries assessed): Brokering/Dealers, Armed Violence, and Final Provisions (all at 2% opposed).
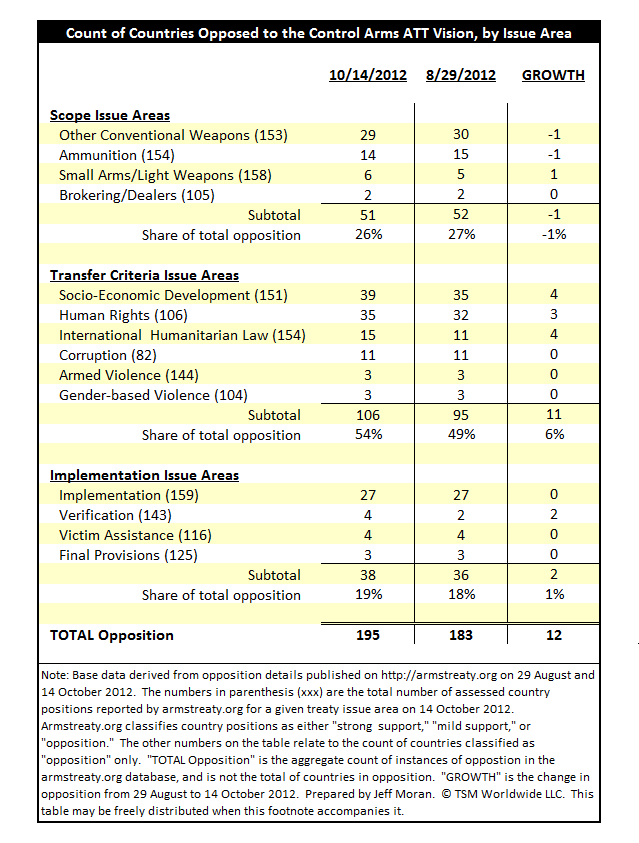
Rightly understood, Control Arms’ own data help to correct the false narrative about why the UN ATT Conference failed to reach consensus this summer. Such data clearly show that the prospects for consensus were grim at best, and are getting worse. The data also suggest that even if the US enthusiastically embraced the final draft ATT, other countries would have probably worked together to prevent consensus anyway.
It is not a giant leap in logic to see that Cuba, Iran, or Venezuela (countries that each oppose many more treaty provisions than the US does) probably would have killed consensus themselves, especially if the United States indicated it was going to sign the treaty. Venezuelan President Hugo Chavez, for one, faced an election within months. Being the consensus breaker would have surely boosted President Chavez’ domestic political standing, and perhaps his image as a regional guardian against outside meddling.
In conclusion, UN ATT Conference died from lack of consensus. This death was due less to failed diplomacy, or pressure by the firearms industry and gun rights groups, than it was the result of many years of abortive advocacy lead by an unraveling UK-based Control Arms campaign. Control Arms’ broad vision for the ATT was more extreme than consensus could sustain. Ultimately, humanitarian groups sabotaged consensus for an ATT by pushing diplomats too hard for far too much and provoked dispositive sovereignty concerns across the Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East in addition to the United States.
Perhaps a more extreme version of the ATT will be born outside the UN altogether. If this happens, it would likely share a destiny not unlike like the 1997 Ottawa Treaty banning anti-personnel landmines. Ottawa was born outside the UN because an anti-personal mine ban did not get traction inside it. Russia, China, and the United States have still not ratified or acceded to the treaty. And while 33 other states have not ratified or acceded to the Ottawa Treaty either, supporters argue that the treaty is emerging as an international norm on its way to acquiring the force of international law over time.[12]
Most likely, within a year, the UK, the lead country responsible for putting the ATT on the UN agenda in 2006, will introduce the draft ATT to the UN General Assembly and seek signatures from countries willing to sign it as is. Unfortunately, regardless of what course the ATT takes, moving forward with an ATT not based on consensus will only serve to divide the international community. As the specter of major conflict looms larger over volatile regions of the world, more division is now the last thing the international community needs.
About The Author
Jeff Moran, a Principal at TSM Worldwide LLC, specializes in the international defense, security, and firearms industries. Previously Mr. Moran was a strategic marketing leader for a multi-billion dollar unit of a public defense & aerospace company, a military diplomat, and a nationally ranked competitive rifle shooter. He is currently studying international law of armed conflict with the Executive LL.M. Program of the Geneva Academy. Earlier this year he completed an Executive Master in International Negotiation from the Graduate Institute of Geneva. Mr. Moran also has an MBA from Emory University’s Goizueta Business School and a BSFS from Georgetown University’s Walsh School of Foreign Service.
End Notes
[1] The First Committee “deals with disarmament, global challenges and threats to peace that affect the international community and seeks out solutions to the challenges in the international security regime.” It meets in October each year. See http://www.un.org/en/ga/first/ for more information about this. Opening day official statements can be found at http://www.un.org/News/Press/docs/2012/gadis3453.doc.htm. Oxfam International has a blog associated with this series of meetings at http://blogs.oxfam.org/en/blogs/12-10-12-fighting-arms-trade-treaty-un-general-assembly. All links last accessed 15 October 2012.
[2] The key deliverable from the UN ATT Conference was an unsigned final draft treaty dated 26 July 2012. This draft is available at http://www.un.org/disarmament/convarms/ATTPrepCom/Documents/PrepCom4%20 Documents/PrepCom%20Report_E_20120307.pdf. Last accessed 14 October 2012.
[3] The Control Arms Campaign is the flagship civil society campaign advocating for an ATT. It started-up in 2003 as a powerful collaboration among the UK offices of Amnesty International, the International Action Network on Small Arms (IANSA), and Oxfam International. In addition to having been funded by a few governments, Control Arms has support from under a 100 mostly Western advocacy groups yet views itself as a “global civil society alliance.” There are many different humanitarian groups and campaigns, but Control Arms is the biggest. Another campaign, the Campaign Against the Arms Trade, is loud and vocal, but is not taken seriously by governments because it advocates for a total ban on the Arms Trade.
[4] Armstreaty.org is the leading ATT negotiations tracking website created by the Control Arms campaign and the Women’s International League for Peace and Freedom. http://armstreaty.org/mapsstates.php. Last accessed 15 October 2012.
[5] Such views underpin many official views found the May 2012 official UN document “Compilation of Views on the Elements of an Arms Trade Treaty (A/CONF.217/2.” http://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/CONF.217/2. Last accessed 15 October 2012.
[6] Here are links to press releases from Reuters, Oxfam, Amnesty International, and Control Arms: http://www.reuters.com/article/2012/07/27/us-arms-treaty-idUSBRE86Q1MW20120727, http://www.oxfam.org/en/pressroom/pressrelease/2012-07-28/battle-arms-trade-treaty-continues-governments-opt-delay-final-dea, http://amnesty.org/en/news/world-powers-delay-landmark-arms-trade-deal-2012-07-27, and http://www.controlarms.org/battle-continues. Sources last accessed 14 October 2012.
[7] Author conducted interviews with numerous diplomats and country delegates in and around the Geneva-based UN disarmament community in 2012. A consistent portrait painted by them was that Control Arms campaigners exhibited a profound lack of collective unity and focus, and that messaging was redundant, superficial, grossly insufficient to help in a technical or practical sense, and largely amounted to a waste of time even for diplomats and delegates who were sympathetic to their cause. Additionally, Control Arms Campaigners undermined their own efforts by insisting on adding controversial provisions to the treaty, such as Victim Assistance, which made consensus all the more unattainable.
[8] Control Arms is described as “unraveling” because, by 2012, Control Arms had essentially disintegrated as a cohesive coalition. This appears to be a key reason for a lack of focus in campaign execution. The proximate cause for this appears to be a case of disintegration due to interpersonal problems and hubris among its leaders, and organizational self-interest. Amnesty International essentially left Control Arms to pursue its own agenda in 2011. This information was corroborated by interviews with several diplomats and an interview with a professional arms trade researcher with direct knowledge of the situation and people concerned, May 2012.
[9] TSM Worldwide LLC conducted a comparative analysis of the website using snapshots taken 29 August and 14 October 2012.
[10] The only Scope issue area the US objected to was the inclusion of ammunition in the treaty. The implementation issue areas the US objects to are Final Provisions and Victim Assistance. Source: armstreaty.org. Last accessed 14 October 2012.
[11] The graphic represents outright country opposition to given issue areas as gauged by Control Arms only. The totals at the bottom of the table are counts of distinct instances of country / issue-area opposition and do not reflect the count of countries opposed to the ATT as a whole.
[12] One group is Handicap International, sponsors of the Campaign to Ban Landmines and co-winner of the 1997 Nobel Peace Prize. http://en.handicap-international.ca/Ottawa-treaty-good-news-and-bad-news_a186.html Last accessed 1 October 2012.
First Published: 17 October 2012
Last Updated: 18 October 2012
Republication and redistribution are authorized when author Jeff Moran and linkable URL http://tsmworldwide.com/consensus-killed/ are cited.
Canada’s NFA to UN: ‘Self-defense is a natural right’
Thursday, August 30th, 2012Original Story Via: TheGunMag.com
Canada’s National Firearms Association was the only Canadian pro-firearms group represented during the non-governmental organization presentations at the Second Review Conference of the Programme of Action to Prevent, Combat and Eradicate the Illicit Trade in Small Arms and Light Weapons. (PoA)
According to NFA President Sheldon Clare, “It was important for the NFA to be present at this conference for four main reasons. First, the PoA is alive and potentially dangerous – this was a well-attended conference and vigilance is critical. Second, it was necessary for us to make sure that there was no attempt to make this the Arms Trade Treaty consolation round, or in any way broaden the scope of the PoA. Third, we needed to make our concerns known about the aims of some to include firearms components and ammunition, and to make it clear that we are speaking out strongly in support of civilian rights of self-defense – the only Canadian organization to do so. The fourth reason we were there was to use our strong voice to support our friends.”
According to Clare, “The government seems to be headed in the right direction. I was pleased to hear the concise and clear presentation by Senior Policy Advisor Kim Joslin of the Canadian Delegation which was in strong support of firearms owners. In particular, Canada supported the US position which opposes including any aspect of components or ammunition being included in the PoA. Government representatives Habib Massoud and Steve Torino will be attending the second week of the conference. It was clear to me in listening to the speeches from delegates that it will be difficult to achieve consensus on several aspects of the PoA‘s implementation plan in the two weeks allotted”.
The NFA and other World Forum (WFSA) members, presented to the UN Conference during the NGO session on Wednesday, August 29 and the text of the speech given by NFA President Sheldon Clare is reproduced below:
STATEMENT TO UNITED NATIONS ON PROGRAMME OF ACTION ON SMALL ARMSS and LIGHT WEAPONS
Madame President, I am Sheldon Clare, President of Canada’s National Firearms Association.
The NFA is Canada’s largest advocacy organization representing the rights of Canadian firearms owners. Our members are concerned that UN attempts to regulate small arms and light weapons are misdirected and will have an unjustifiably harmful effect upon the ability of free people to have access to firearms and ammunition for perfectly legitimate purposes. The NFA rejects as false that civilian access to small arms is the problem.
Canada’s National Firearms Association (NFA) recommends that controls on small arms and light weapons be limited solely to major crew-served weapon systems possessed or sold by nation states – not individually operated firearms owned or desired to be owned by civilians, also called non-state actors. The rights and property of Canadians, and our firearms businesses engaged in the lawful trade in firearms and ammunition, including surplus firearms and ammunition, must not be subject to UN edict or control. Quite simply, firearms ownership and use are matters of national sovereignty, civil freedoms, property rights, and are related to national culture. Also, control of ammunition, including marking beyond caliber, date, and manufacturer would be excessive; it is unreasonable, unnecessary, and fiscally impossible to uniquely mark ammunition.
Small arms in civilian hands allow people to defend themselves from aggression. Self-defense is a natural right of all individuals. This is especially important in the event of unrest and disorder, or in case of state-mandated crimes against humanity. Civilian ownership of arms is an important factor in preventing and limiting the effect of government-encouraged murders such as what occurred in Srebrenica and Rwanda. Disarmed in Srebrenica by UN peacekeepers and in Rwanda by their own government, these people were helpless in the face of organized aggression, especially when in both cases the UN was powerless to provide protection. While governments need to act against terrorism, disarming civilians violates fundamental democratic principles. Perhaps Governments should deal with unrest by addressing the economic situations, political differences, and human rights issues that contribute to people agitating for change rather than engaging in one size fits all solutions affecting the rights of free people to own and use firearms.
Thank you for your consideration Madame President.”
Clare concluded: “Other matters to be watchful of are the UN International Small Arms Control Standards, (see http://www.smallarmsstandards.org/isacs/) and what happens with the Arms Trade Treaty talks (ATT) which broke up without consensus in July. There will need to be a vote at the General Assembly if it is to come back next year, which may not be possible due to the UN’s two year budgetary cycle. Simply put, there may not be much support to reopen the ATT so soon in the face of no consensus. Nonetheless, strange things happen at the UN and the NFA has been present to protect the civil and property rights of Canadian Firearms Owners.”
Governments not people craft UN Arms Trade Treaty
Wednesday, August 8th, 2012Original Story Via: TheGunMag.com
By Joseph P. Tartaro
Executive Editor
Perhaps the United Nations should have a motto that reflects its focus on “government stability” and the balance of power between the people of the world and their respective governments.
I’d suggest the UN consider clearly stating, “The most despicable government we’ve ever known was pretty good.” If you need evidence beyond the fact that the lambs have been feeding at the same trough as the crocodiles all of these years, just look what the UN did as the much anticipated and dreaded conference on a binding Arms Trade Treat (ATT) began in July.
With the shadow of Syrian repression cast across most news media in the world and clouding the ATT talks, the UN turned to Iran to help negotiate a global arms treaty in a move that is drawing scorn and ridicule around the globe. But apparently not among the striped-pants diplomats meeting in New York City.
The appointment was made by members of the UN Conference on the ATT shortly after the month-long conference began in July. The committee to which Iran was appointed is tasked with coming up with a treaty regulating the international trade of conventional small arms and, proponents hope, ammunition.
“Right after a UN Security Council report found Iran guilty of illegally transferring guns and bombs to Syria, which is now murdering thousands of its own people, it defies logic, morality, and common sense for the UN to now elect this same regime to a global post in the regulation of arms transfers,” said Hillel Neuer, executive director of UN Watch, a non-governmental monitoring group based in Geneva.
“This is like choosing Bernie Madoff to police fraud on the stock market.
And the UN’s scandalous choice of Iran is exactly why we fear that Syria’s declared bid for a UN Human Rights Council seat is not impossible.” The 15-nation committee is led by Argentina, which serves as president, and includes the US, Iran, China, and Russia as nations that serve as vice presidents.
UN Watch called on UN Secretary- General Ban Ki-moon to condemn the decision to name Iran to the committee.
“He should remind the conference that the Security Council has imposed four rounds of sanctions on Iran for refusing to halt its prohibited nuclear program, and that Iran continues to defy the international community through illegal arms shipments to the murderous Assad regime,” Neuer said.
US officials played down the significance of the appointment.
“Obviously we oppose (Iran’s appointment), but it’s a symbolic position with little impact on a month-long negotiation that must be decided by consensus,” one senior State Department official told Fox News.
“It will ultimately face the approval of the United States regardless of which country holds one of 14 powerless vice president positions. At that point, we will be looking for an arms trade treaty that makes the legitimate global weapons trade safer by bringing the rest of the world’s arms trade regulations up to the high US standard.” However, two weeks into the deliberations on the ATT, there seems to be a wide divergence of position by different governments. There is no guarantee the negotiations now in progress will produce a treaty, let alone a good one. In February, preparatory talks on the ground rules for this month’s talks nearly collapsed due to procedural wrangling and other disagreements.
In the end, the US and other countries succeeded in ensuring the treaty must be approved unanimously, so any one country can effectively veto a deal.
In spite of Iran and Syria, there are still deep divisions on key issues to be tackled in the treaty negotiations, such as whether human rights should be a mandatory criterion for determining whether governments should permit weapons exports to specific countries.
China wants to exempt small arms, while several Middle East states oppose making compliance with human rights norms a mandatory criterion for allowing arms deliveries. Meanwhile, Canada wants to exclude civilian small arms and ammunition altogether.
Britain has joined France, Germany and Sweden in calling for a solid, effective and legally binding treaty.
According to Peter Brookes of the Heritage Foundation, a treaty would damage US foreign policy and prevent it helping friends such as Taiwan. But he noted the treaty was not yet a done deal.
“Diplomats will natter away about it all month over cappuccinos in Turtle Bay,” he wrote. “But the White House isn’t doing the country any favors by playing footsie with a UN effort to take aim at our liberties and disarm our foreign policy.” Meanwhile, many organizations opposed to the treaty have been allowed to speak at the UN, and more than 130 congressmen, led by Rep.
Mike Kelly (R-PA), signed a letter sent to President Barack Obama in early July expressing their opposition to a UN arms trade treaty if it violates US gun owner rights and sovereignty.
The letter includes specific demands— that the treaty leave out small arms and ammunition and recognize an individual’s right to self-defense.
The Obama administration has claimed that there are safeguards to their treaty approach, but the safeguard is insufficient for opponents of the US participation, not least because UN talks invariably involve compromise.
“The administration swears they have a whole bunch of red lines, and they will block consensus if anyone crosses them,” said a government relations consultant as senior associate with the Commonwealth Consulting Corporation.
“But the dynamics of international negotiations are that once you get 90% of what you seek, you say, ‘Maybe there is a way we can finesse the final 10%.’ ” A clause permitting arms transfers solely between UN member states would allow UN member China to object to US arms sales to Taiwan, a non-UN member that China considers to be a renegade province.
This would be highly problematic for the US at a time when Beijing is engaged in an unprecedented arms buildup.
Another fear is that Arab or other states critical of Israel may use any treaty language on human rights standards to argue against US arms transfers to the Israeli government—as they currently use the UN Human Rights Council to condemn Israel.
US gun lobby concern focus on the emphasis the treaty places on governmental— as opposed to individual— rights to guns, according to Wayne LaPierre, NRA executive vice president.
“They’re trying to impose a UN policy that gives guns to the governments— but the UN doesn’t in turn make moral judgments as to whether these governments are good or bad,” he said.
“If you’re the government, you get the guns, if you’re a civilian, you don’t.
This will just end up helping evil governments and tyrants.”
UN ATT: Anti-gunners not finished with push for global gun control
Wednesday, August 1st, 2012Original Story Via: Dave Workman, Seattle Gun Rights Examiner
Despite Friday’s breakdown on the global Arms Trade Treaty, international gun control proponents are determined to push their agenda, according to a report carried in the Saturday issue of the Seattle P-I.com.
Alan Gottlieb, chairman of the Bellevue-based Citizens Committee for the Right to Keep and Bear Arms, watched it all unfold at the United Nations, tipping this column early in the day that the United States would not be signing on, as American anti-gunners had hoped. He told Examiner via e-mail and telephone that the ATT’s momentum hit a massive speed bump because the final draft of the treaty was not produced until late in the day.
Anti-gunners are blaming the National Rifle Association for riling up its members, but that’s hardly the entire story. It’s just that the NRA is an easy target. The NRA did a remarkably effective job alerting its members, and NRA Executive Vice President Wayne LaPierre left no doubt when he spoke at the U.N. that his organization would fight this treaty with every available resource.
Amnesty International’s Suzanne Trimel, quoted by the Huffington Post, accused the NRA of “spreading lies” about the treaty.
“Basically,” Trimel reportedly stated, “what they’re saying is that the arms trade treaty will have some impact on domestic, Second Amendment gun rights. And that is just false, completely false.”
Gottlieb’s CCRKBA also mounted a massive grassroots effort to thwart the treaty, and gun owners responded by calling Capitol Hill. This resulted in a groundswell of gun owner fury over a document that was far too much in flux. One wonders what Trimel might say about that organization.
And in the background, domestic firearms and ammunition manufacturers were none-too-thrilled with the proposed treaty, either because it could have had a severe impact on their international business. Likewise, European gun makers were not happy because they sell a lot of firearms here in the United States and elsewhere.
This column’s revelation that the treaty would create a new gun control “secretariat” — translation: a new international bureaucracy — raised even more alarms. That detail was buried several pages back in the treaty draft, and as the saying goes, the Devil is in the details.
The meetings actually went on for about three weeks with little or no movement until the past few days. Gottlieb, who was at the U.N. with his wife, Julianne Versnel, both told Examiner that many people were frustrated at the process. Because the final treaty draft was not delivered until late Thursday afternoon, people simply did not have the opportunity to study it. Versnel noted that other countries — China and Russia most notably — threw up roadblocks as well.
Global gun control proponents are determined to bring this treaty proposal back to the table in September. They are an unhappy lot, so much so that Suzanne Nossel, executive director of Amnesty International USA, felt compelled to say this:
“This was stunning cowardice by the Obama administration, which at the last minute did an about-face and scuttled progress toward a global arms treaty, just as it reached the finish line. It’s a staggering abdication of leadership by the world’s largest exporter of conventional weapons to pull the plug on the talks just as they were nearing an historic breakthrough.”—Suzanne Nossel, quoted by USAToday.
The irony of this statement is perhaps most stunning to American gun owners, who see the Obama administration as the archenemy of gun rights. It was, after all, President Obama who appointed two liberal anti-gunners to the U.S. Supreme Court. It was Mr. Obama who provided last-minute cover to embattled Attorney General Eric Holder in his effort to withhold documents from the Fast and Furious investigation. It was the president who said in 2009 that he supported the ATT and indicated he would sign it.
Now the president is taking a verbal beating from those with whom he might be most closely allied, both politically and philosophically.
Victoria Nuland, spokeswoman for Hillary Clinton’s State Department is quoted by the Associated Press story that appears in the Seattle P-I.com. She reportedly said the U.S. — meaning the Obama administration — wants another round of negotiations next year, as in “after the November election.”
Gun owners are coming to full realization just how important the election is, not only on domestic issues but also on an international scale. Because this treaty still has a genuine possibility of resurrection, it remains a threat and in the collective mind of the firearms community the most effective way to stop it is to replace the administration that wants to sign it.
NFA Canada shares thoughts on the UN ATT
Monday, July 30th, 2012Original Story Via: National Firearms Association (Canada)
UN Arms Trade Treaty Talks Close Without Consensus
The United Nations talks on an Arms Trade Treaty ended today without consensus on any of the latest proposed treaty drafts. The UN’s self-imposed deadline of July 27 saw considerable disagreement remaining on the part of many nations as to the content and goals of various draft treaty language.
Speaking from Orangeville, Ontario NFA President Sheldon Clare stated that, “While many may view this as a relief, it is important to realize that there is still significant pressure from many anti-gun NGOs and governments to achieve such a treaty. In short, the international and domestic firearms communities must continue to be informed about what happens next as part of the larger UN programs of disarmament and any potential effect on civilians who own firearms.”
Clare praised the Canadian delegation, “Canada’s National Firearms Association wishes to acknowledge the professionalism and patience of the Canadian government’s delegation during what were clearly very difficult negotiations to achieve a treaty that would impose “no new burdens” on Canadians.” He continued, “While the NFA has stronger views on the talks than some of those of the government, I believe that Canadians were well served by our national representatives. In particular, the Canadian delegation was vocal in supporting the NFA’s right to have our voice heard at the talks.”
Mr. Clare continued, “The key question for Canadians is what will happen next. Canada’s National Firearms Association will be watching the UN’s next moves and it is important that all firearms owners stay tuned for new developments. One thing is clear, vigilance is important to ensure that we are able to fully protect all aspects of our rights and freedoms.”
In addition to its participation at the UN with the World Forum on the Future of Sport Shooting Activities, Canada’s National Firearms Association is a founding member of The International Association for the Protection of Civilian Arms Rights (IAPCAR) which includes many national and international organizations promoting civilian ownership of firearms. At over 62,000 members, Canada’s National Firearms Association is this country’s largest advocacy organization promoting the rights and freedoms of all responsible firearm owners and users.
For more information contact:
Blair Hagen, Executive VP Communications, 604-753-8682 Blair@nfa.ca
Sheldon Clare, President, 250-981-1841 Sheldon@nfa.ca
Canada’s NFA toll-free number – 1-877-818-0393
NFA Website: www.nfa.ca
BREAKING NEWS: CCRKBA CREDITS GRASSROOTS FOR U.S. DECISION TO NOT SIGN ARMS TREATY
Friday, July 27th, 2012Original Story Via: TheGunMag.com
The Citizens Committee for the Right to Keep and Bear Arms today applauds the decision by the United States to not sign the proposed International Arms Trade Treaty, and CCRKBA credits grassroots action for the gun rights victory.
CCRKBA Chairman Alan Gottlieb, who is at the United Nations in New York, said the announcement came Friday morning after a week of intense negotiations.
“I think the grassroots surge by American gun owners against this treaty convinced our government to not sign this document,” Gottlieb said. “The proposed treaty, as written, poses serious problems for our gun rights, and the sovereignty of our Second Amendment.”
CCRKBA has been active in raising public awareness about the proposed treaty, and Gottlieb said he is proud of members and supporters who made “stepped up to the plate” and contacted their U.S. senators.
“This is freedom in action,” Gottlieb stated. “We are gratified that so many did so much to protect their Second Amendment rights from an international gun rights grab.
International gun banners pulling out all stops at UN
Thursday, July 26th, 2012Original Story Via: TheGunMag.com
By Dave Workman
Senior Editor
The gloves have come off at the United Nations as negotiations over the proposed global Arms Trade Treaty (ATT) are moving toward a climax, and two leading gun rights advocates on the scene are convinced treaty proponents want to include small arms and ammunition in the document, and slip around the Second Amendment.
Alan Gottlieb, founder and executive vice president of the Second Amendment Foundation, told TGM that, “Some movement in our direction is anticipated, but it will not be enough to make a difference. These would be minor modifications to placate us, but they will not be enough to address the concerns of American gun owners.”
“This is a blatant attempt to negate the recent Second Amendment court victories we’ve had in the United States, and to get around Second Amendment protections,” he asserted.
His wife, Julianne Versnel, said the ATT “is, in essence, an attempt by the rest of the world to impose their view of civilian firearms ownership on us, and negate the Second Amendment.”
They are at the UN representing the Citizens Committee for the Right to Keep and Bear Arms, the Second Amendment Foundation and the International Association for the Protection of Civilian Arms Rights (IAPCAR). Both helped create IAPCAR, which now has member organizations around the world.
A coalition of global gun control organizations is pushing for the most extreme language and tenets in the treaty, which is supposed to be signed this week. That group includes International Action Network on Small Arms (IANSA) and Oxfam International and Control Arms. The latter group is apparently responsible for a handout depicting their vision of the treaty provisions highlighted in Olympics-style rings.
Ominously, two of those items are “Arms and Bullets” and “Global Standards Over National Views.” The former alludes to privately owned firearms, and the latter is a veiled but direct threat to the Second Amendment, Gottlieb said.
Various gun rights organizations have been lobbying against this treaty for weeks. If the Obama administration signs it, the document must still be ratified by the U.S. Senate, and after intense lobbying by the National Rifle Association, that doesn’t seem likely.
But with less than four months to go before the national elections, Barack Obama is painting himself into an ever-tightening corner with American gun owners. That represents a significant and influential voting bloc, and a global gun control treaty could easily push many undecided voters into the Romney camp.
NFA Warns of Problems With UN Arms Trade Treaty
Wednesday, July 25th, 2012NFA Warns of problems with UN Arms Trade Treaty
25 July 2012
A near final draft and the closing days of the UN Arms Trade Treaty talks could spell trouble for Canadian interests. There is tremendous pressure to conclude a deal by July 27 and if the latest draft is any indication, the deal will not be a good one for Canadians.
“The draft treaty still affects civilian ownership of firearms and could cause trouble for Canadians travelling with firearms,” according to Sheldon Clare, President of Canada’s National Firearms Association who was present for part of the talks. “Even more significantly though, are clauses which would establish an expensive and intrusive Implementation Support Unit, a body which would be engaged in keeping firearms trade records. The ISU would be a likely conduit for providing money to unscrupulous regimes from UN coffers partially funded by Canadian taxpayers. That is certainly not something that Canadians want or need.”
Clare continued, “One of the most potentially dangerous clauses is the proposed amending formula which under Article 20 introduces a two-thirds majority requirement to amend the ATT. Such a clause is a direct threat to national sovereignty in that it removes the traditional need for consensus in UN decision making. It could easily lead to despots and dictators making amendments that would be binding on Europe and North America. When combined with Article 23 which would mean that even countries that don’t sign it are subject to it, we have a clear step towards a dangerous system of world governance that would harm the interests of Canada and individual Canadians.“
“In addition, there are aspects of the draft treaty that could prevent Canada from providing aid to its needy allies, especially if such aid conflicted with the aims of countries opposed to Canadian values. The recent draft of the Arms Trade Treaty is bad for Canada and Canadians, and our government should not sign it,” stated Mr. Clare. “While governments need to act against terrorism, perhaps better ways to deal with unrest would be to address the economic situations, political differences, and human rights issues that contribute to people agitating for change.”
“A global ATT would only be in the interests of those who would seek economic advantage by limiting market opportunity and of regimes who would use such a treaty to disarm their citizens in order to rule through fear.”
In addition to its participation at the UN with the World Forum on the Future of Sport Shooting Activities, Canada’s National Firearms Association is a founding member of The International Association for the Protection of Civilian Arms Rights (IAPCAR) which includes many national and international organizations promoting civilian ownership of firearms. At over 62,000 members, Canada’s National Firearms Association is this country’s largest advocacy organization promoting the rights and freedoms of all responsible firearm owners and users.
For more information contact:
Blair Hagen, Executive VP Communications, 604-753-8682 Blair@nfa.ca
Sheldon Clare, President, 250-981-1841 Sheldon@nfa.ca
Canada’s NFA toll-free number – 1-877-818-0393
NFA Website: www.nfa.ca
BREAKING NEWS: UN Arms Trade Treaty – Full Proposed Document
Tuesday, July 24th, 2012PREAMBLE
The States Parties to this Treaty.
- Guided by the purposes and principles of the Charter of the United Nations.
- Recalling that the charter of the UN promotes the establishment and maintenance of international peace and security with the least diversion for armaments of the world’s human and economic resources;
- Reaffirming the obligation of all State Parties to settle their international disputes by peaceful means in such a manner that international peace and security, and justice, are not endangered, in accordance with the Charter of the UN;
- Underlining the need to prevent, combat and eradicate the illicit trade of conventional arms and to prevent their diversion to illegal and unauthorized end use, such as terrorism and organized crime;
- Recognizing the legitimate political, security, economic and commercial rights and interests of States in the international trade of conventional arms;
- Reaffirming the sovereign right and responsibility of any State to regulate and control transfers of conventional arms that take place exclusively within its territory pursuant to its own legal or constitutional systems;
- Recognizing that development, human rights and peace and security, which are three pillars of the United Nations, are interlinked and mutually reinforcing.
- Recalling the United Nations Disarmament Commission guidelines on international arms transfers adopted by the General Assembly;
- Noting the contribution made by the 2001 UN Programme of Action to preventing combating and eradicating the illicit trade in small arms and light weapons in all its aspects, as well as the 2001 Protocol against the illicit manufacturing of and trafficking in Firearms, their parts and components and ammunition, supplementing the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime;
- Recognizing the security, social, economic and humanitarian consequences of the illicit trade in and unregulated trade of conventional arms;
- Recognizing the challenges faced by victims of armed conflict and their need for adequate care, rehabilitation and social and economic inclusion;
- Bearing in mind that the women and children are particularly affected in situations of conflict and armed violence;
- Emphasizing that nothing in this treaty prevents States from exercising their right to adopt additional more rigorous measures consistent with the purpose of this Treaty;
- Recognizing the legitimate international trade and lawful private ownership and use of conventional arms exclusively for, inter alia, recreational, cultural, historical and sporting activities for States where such ownership and use are permitted or protected by law;
- Recognizing the active role that non-governmental organizations and civil society can play in furthering the goals and objectives of this Treaty; and
16. Emphasizing that regulation of the international trade in conventional arms should not
hamper international cooperation and legitimate trade in material, equipment and technology
for peaceful purposes;
Have agreed as follows:
Principles
Guided by the Purposes and Principles of the Charter of the United Nations, States Parties, In promoting the goals and objectives of this Treaty and implementing its provisions, shall act in accordance with the following principles:
- The inherent rights of all States to individual or collective self-defense;
2. Settlement of individual disputes by peaceful means in such a manner that international peace and security, and justice, are not endangered;
3. The rights and obligations of States under applicable international law, including international humanitarian law and international human rights law;
4. The responsibility of all States, in accordance with their respective international obligations, to effectively regulate and control international transfer of conventional arms as well as the primary responsibility of all States to in establishing and implementing their respective national export control systems; and
5. The necessity to implement this Treaty consistently and effectively and in a universal, objective and non-discriminatory manner.
Article 1
Goals and Objectives
Cognizant of the need to prevent and combat the diversion of conventional arms into the illicit market r to unauthorized end users through the improvement of regulation on the international trade in conventional arms,
The goals and objectives of this Treaty are:
– For States Parties to establish the highest possible common standards for regulating or improving regulation of the international trade in conventional arms;
– To prevent, combat and eradicate the illicit trade in conventional arms and their diversion to illegal and unauthorized end use;
In order to:
– Contribute to international and regional peace, security and stability;
– Avoid that the international trade in conventional arms contributes to human suffering;
– Promote cooperation, transparency and responsibility of States Parties in the trade in conventional arms, thus building confidence among States Parties,
Article 2
– A. Covered Items
– 1. This Treaty shall apply to all conventional arms within the following categories:
– a. Battle Tanks
– b. Armored combat vehicles
– c. Large-caliber Artillery systems
– d. Combat aircraft
– e. Attack helicopters
– f. Warships
– g. Missiles and missile launchers
– h. Small Arms and Light Weapons
– 2. Each State Party Shall establish and Maintain a national control system to regulate the export of munitions to the extent necessary to ensure that national controls on the export of the conventional arms covered by Paragraph a1 (a)-(h) are not circumvented by the export of munitions for those conventional arms.
– 3. Each State Party shall establish and maintain a national control system to regulate the export of parts and components to the extent necessary to ensure that national controls on the export of the conventional arms covered by Paragraph A1 are not circumvented by the export of parts and components of those items.
– 4. Each State Party shall establish or update, as appropriate, and maintain a national control list that shall include the items that fall within Paragraph 1 above, as defined on a national basis, based on relevant UN instruments at a minimum. Each State Party shall publish its control list to the extent permitted by national law.
– B. Covered Activities
– 1. This Treaty shall apply to those activities of the international trade in conventional arms covered in paragraph a1 above, and set out in Articles 6-10, hereafter referred to as “transfer.”
– 2. This Treaty shall not apply to the international movement of conventional arms by a State Party or its agents for its armed forces or law enforcement authorities operating outside its national territories, provided they remain under the State Party’s ownership.
Article 3
Prohibited Transfers
- A State Party shall not authorize any transfer of conventional arms within the scope of this Treaty if the transfer would violate any obligation under any measure adopted by the United Nations Security Council acting under Chapter VII of the Charter of the United Nations, in particular arms embargoes.
- A State Party shall not authorize any transfer of conventional arms within the scope of this Treaty if the transfer would violate its relevant international obligations, under international agreements, to which it is a Party, in particular those relating to the international transfer of, or illicit trafficking in, conventional arms.
- A State Party shall not authorize a transfer of conventional arms within the scope of this Treaty for the purpose of facilitating the commission of genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes constituting grave breaches of the Geneva Conventions of 1949, or serious violations of Common Article 3 of the Geneva Convention of 1949.
Article 4
National Assessment
- Each State Party, in considering whether to authorize an export of conventional arms within the scope of this Treaty, shall, prior to authorization and through national control systems, make an assessment specific to the circumstances of the transfer based on the following criteria:
- Whether the proposed export of conventional arms would:
- Be used to commit or facilitate serious violations of international humanitarian law;
- Be used to commit or facilitate serious violations of international human rights law;
- Contribute to peace and security;
- Be used to commit or facilitate an act constituting an offense under international conventions and protocols relating to terrorism or transnational organized crime, to which the transferring State is a Party;
- In making the assessment, the transferring State Party shall apply the criteria set out in Paragraph 2 consistently and in an objective and non-discriminatory manner and in accordance with the principles set out in this Treaty, taking into account relevant factors, including information provided by the importing State.
4. In assessing the risk pursuant to Paragraph 2, the transferring State Party may also take into consideration the establishment of risk mitigation measures including confidence-building measures and jointly developed programs by the exporting and importing State.
5. If in the view of the authorizing State Party, this assessment, which would include any actions that may be taken in accordance with Paragraph 4, constitutes a substantial risk, the State Party shall not authorize the transfer.
Article 5
Additional Obligations
- Each State Party, when authorizing an export, shall consider taking feasible measures, including joint actions with other States involved in the transfer, to avoid the transferred arms:
- being diverted to the illicit market;
- be used to commit or facilitate gender-based violence or violence against children;
- become subject to corrupt practices; or
- adversely impact the development of the recipient State.
Article 6
General Implementation
- Each State Party shall implement this Treaty in a consistent, objective and non-discriminatory manner in accordance with the goals and objectives of this Treaty;
- The implementation of this Treaty shall not prejudice previous or future obligations undertaken with regards to international instruments, provided that those obligations are consistent with the goals and objectives of this Treaty. This Treaty shall not be cited as grounds for voiding contractual obligations under defense cooperation agreements concluded by States Parties to this Treaty.
- Each State Party shall take all appropriate legislative and administrative measures necessary to implement the provisions of this Treaty and designate competent national authorities in order to have an effective, transparent and predictable national control system regulating the transfer of conventional arms;
- Each State Party shall establish one or more national contact points to exchange information on matters related to the implementation of this Treaty. A State Party shall notify the Implementation Support Unit (See Article 13) of its national contact point(s) and keep the information updated.
- State Parties involved in a transfer of conventional arms shall, in a manner consistent with the principles of this Treaty, take appropriate measures to prevent diversion to the illicit market or to unauthorized end-users. All State Parties shall cooperate, as appropriate, with the exporting State to that end.
- . If a diversion is detected the State or States Parties that made the decision shall verify the State or States Parties that could be affected by such diversion, in particulate those State Parties that are involved in the transfer, without delay.
- Each State Party shall take the appropriate measures, within national laws and regulations, to regulate transfers of conventional arms within the scope of the Treaty.
Article 7
Export
- Each State Party shall conduct risk assessments, as detailed in Articles 4 and 5, whether to grant authorizations for the transfer of conventional arms under the scope of this Treaty. State Parties shall apply Articles 3-5 consistently, taking into account all relevant information, including the nature and potential use of the items to be transferred and the verified end-user in the country of final destination.
- Each State Party shall take measures to ensure all authorizations for the export of conventional arms under the scope of the Treaty are detailed and issued prior to the export. Appropriate and relevant details of the authorization shall be made available to the importing, transit and transshipment State Parties, upon request.
Article 8
Import
- Importing State Parties shall take measures to ensure that appropriate and relevant information is provided, upon request, to the exporting State Party to assist the exporting State in its criteria assessment and to assist in verifying end users.
- State Parties shall put in place adequate measures that will allow them, where necessary, to monitor and control imports of items covered by the scope of the Treaty. State Parties shall also adopt appropriate measures to prevent the diversion of imported items to unauthorized end users or to the illicit market.
- Importing State Parties may request, where necessary, information from the exporting State Party concerning potential authorizations.
Article 9
Brokering
- Each State Party shall take the appropriate measures, within national laws and regulations, to control brokering taking place under its jurisdiction for conventional arms within the scope of this Treaty.
Article 10
Transit and Transshipment
- Each State Party shall adopt appropriate legislative, administrative or other measures to monitor and control, where necessary and feasible, conventional arms covered by this Treaty that transit or transship through territory under its jurisdiction, consistent with international law with due regard for innocent passage and transit passage;
- Importing and exporting States Parties shall cooperate and exchange information, where feasible and upon request, to transit and transshipment States Parties, in order to mitigate the risk of discretion;
Article 11
Reporting, Record Keeping and Transparency
- Each State Party shall maintain records in accordance with its national laws and regardless of the items referred to in Article 2, Paragraph A, with regards to conventional arms authorization or exports, and where feasible of those items transferred to their territory as the final destination, or that are authorized to transit or transship their territory, respectively.
- Such records may contain: quantity, value, model/type, authorized arms transfers, arms actually transferred, details of exporting State(s), recipient State(s), and end users as appropriate. Records shall be kept for a minimum of ten years, or consistent with other international commitments applicable to the State Party.
- States Parties may report to the Implementation Support Unit on an annual basis any actions taken to address the diversion of conventional arms to the illicit market.
- Each State Party shall, within the first year after entry into force of this Treaty for that State Party, provide an initial report to States Parties of relevant activities undertaken in order to implement this Treaty; including inter alia, domestic laws, regulations and administrative measures. States Parties shall report any new activities undertaken in order to implement this Treaty, when appropriate. Reports shall be distributed and made public by the Implementation Support Unit.
- Each State Party shall submit annually to the Implementation Support Unit by 31 May a report for the preceding calendar year concerning the authorization or actual transfer of items included in Article 2, Paragraph A1. Reports shall be distributed and made public by the Implementation Support Unit. The report submitted to the Implementation Support Unit may contain the same type of information submitted by the State Party to other relevant UN bodies, including the UN Register of Conventional Arms. Reports will be consistent with national security sensitivities or be commercially sensitive.
ARTICLE 12
ENFORCEMENT
- Each State Party shall adopt national legislation or other appropriate national measures regulations and policies as may be necessary to implement the obligations of this Treaty.
ARTICLE 13
IMPLEMENTATION SUPPORT UNIT
- This Treaty hereby establishes an Implementation Support Unit to assist States Parties in its implementation.
- The ISU shall consist of adequate staff, with necessary expertise to ensure the mandate entrusted to it can be effectively undertaken, with the core costs funded by States Parties.
- The implementation Support Unit, within a minimized structure and responsible to States Parties, shall undertake the responsibilities assigned to it in this Treaty, inter alia:
- Receive distribute reports, on behalf of the Depository, and make them publicly available;
- Maintain and Distribute regularly to States Parties the up-to-date list of national contact points;
- Facilitate the matching of offers and requests of assistance for Treaty implementation and promote international cooperation as requested;
- Facilitate the work of the Conference of States Parties, including making arrangements and providing the necessary service es for meetings under this Treaty; and
- Perform other duties as mandated by the Conference of States Parties.
ARTICLE 14
INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION
- States Parties shall designate national points of contact to act as a liaison on matters relating to the implementation of this Treaty.
- States Parties shall cooperate closely with one another, as appropriate, to enhance the implementation of this Treaty consistent with their respective security interests and legal and administrative systems.
States Parties are encouraged to facilitate international cooperation, including the exchange of information on matters of mutual interest regarding the implementation and application of this Treaty in accordance with their national legal system. Such voluntary exchange of information may include, inter alia, information on national implementation measures as well as information on specific exporters, importers and brokers and on any prosecutions brought domestically, consistent with commercial and proprietary protections and domestic laws, regulations and respective legal and administrative systems.
4. Each State Party is encouraged to maintain consultations and to share information, as appropriate, to support the implementation of this Treaty, including through their national contact points.
5. States Parties shall cooperate to enforce the provisions of this Treaty and combat breaches of this Treaty, including sharing information regarding illicit activities and actors to assist national enforcement and to counter and prevent diversion. States Parties may also exchange information on lessons learned in relation to any aspect of this Treaty, to develop best practices to assist national implementation.
Article 15
International Assistance
- In fulfilling the obligation of this Treaty, States Parties may seek, inter alia, legal assistance, legislative assistance, technical assistance, institutional capacity building, material assistance or financial assistance. States, in a position to do so, shall provide such assistance. States Parties may contribute resources to a voluntary trust fund to assist requesting States Parties requiring such assistance to implement the Treaty.
- States Parties shall afford one another the widest measure of assistance, consistent with their respective legal and administrative systems, in investigations, prosecutions and judicial proceedings in relation to the violations of the national measures implemented to comply with obligations under of the provisions of this Treaty.
- Each State Party may offer or receive assistance, inter alia, through the United Nations international, regional, subregional or national organizations, non-governmental organizations or on a bi-lateral basis. Such assistance may include technical, financial, material and other forms of assistance as needed, upon request.
Article 16
Signature, Ratification, Acceptance, Approval or Accession
- This Treaty shall be open for signature on [date] at the United Nations Headquarters in New York by all States and regional integration organizations.
- This Treaty is subject to ratification, acceptance or approval of the Signatories.
- This Treaty shall be open for accession by any state and regional integration organization that has not signed the Treaty.
4. The instruments of ratification, acceptance, approval or accession shall be deposited with the Depositary.
5. The Depositary shall promptly inform all signatory and acceding States and regional integration organizations of the date of each signature, the date of deposit of each instrument of ratification, acceptance, approval or accession and the date of the entry into force of this Treaty, and of the receipt of notices.
6. “Regional integration organization” shall mean an organization constituted by sovereign States of a given region, to which its Member States have transferred competence in respect of matters governed by this Treaty and which has been duly authorized, in accordance with its internal procedures, to sign, ratify, accept, approve or accede to it.
7. At the time of its ratification, acceptance, approval or accession, a regional integration organization shall declare the extent of its competence with respect to matters governed by this Treaty. Such organizations shall also inform the Depositary of any relevant modifications in the extent of it competence.
8. References to “State Parties” in the present Treaty shall apply to such organizations within the limits of their competence.
Article 17
Entry into Force
- This Treaty shall enter into force thirty days following the date of the deposit of the sixty-fifth instrument of ratification, acceptance or approval with the Depositary.
- For any State or regional integration organization that deposits its instruments of accession subsequent to the entry into force of the Treaty, the Treaty shall enter into force thirty days following the date of deposit of its instruments of accession.
- For the purpose of Paragraph 1 and 2 above, any instrument deposited by a regional integration organization shall not be counted as additional to those deposited by Member States of that organization.
Article 18
Withdrawal and Duration
- This Treaty shall be of unlimited duration.
- Each State Party shall, in exercising its national sovereignty, have the right to withdraw from this Convention. It shall give notice of such withdrawal to all other States Parties from this Convention. It shall give notice of such withdrawal to all other States Parties and to the Depositary. The instrument of withdrawal shall include a full explanation of the reasons motivating this withdrawal.
- A state shall not be discharged, by reason of its withdrawal, from the obligations arising from this treaty while it was a party to the Treaty, including any financial obligations, which may have accrued.
Article 19
Reservations
- Each State party, in exercising its national sovereignty, may formulate reservations unless the reservation is incompatible with the object and purpose of this Treaty.
Article 20
Amendments
- At any time after the Treaty’s entry into force, a State Party may propose an amendment to this Treaty.
- Any proposed amendment shall be submitted in writing to the Depository, which will then circulate the proposal to all States Parties, not less than 180 days before next meeting of the Conference of States Parties. The amendment shall be considered at the next Conference of States Parties if a majority of States Parties notify the Implementation Support Unit that they support further consideration of the proposal no later than 180 days after its circulation by the Depositary.
- Any amendment to this Treaty shall be adopted by consensus, or if consensus is not achieved, by two-thirds of the States Parties present and voting at the Conference of States Parties. The Depositary shall communicate any amendment to all States Parties.
- A proposed amendment adopted in accordance with Paragraph 3 of this Article shall enter into force for all States Parties to the Treaty that have accepted it, upon deposit with the Depositary. Thereafter, it shall enter into force for any remaining State Party on the date of deposit of its instrument of accession.
Article 21
Conference of States Parties
- The Conference of States Parties shall be convened not later than once a year following the entry into force of this Treaty. The Conference of States Parties shall adopt rules of procedure and rules governing its activities, including the frequency of meetings and rules concerning payment of expenses incurred in carrying out those activities.
The Conference of States Parties shall:
a. Consider and adopt recommendations regarding the implementation of this Treaty, in particular the promotion of its universality; TR
b. Consider amendments to this Treaty;
c. Consider and decide the work and budget of the Implementation Support Unit;
d. Consider the establishment of any subsidiary bodies as may be necessary to improve the functioning of the Treaty;
e. Perform any other function consistent with this Treaty.
3. If circumstances merit, an exceptional meeting of the State Parties may be convened if required and resources allow.
Article 22
Dispute Settlement
- States Parties shall consult and cooperate with each other to settle any dispute that may arise with regard to the interpretation or application of this Treaty.
- States Parties shall settle any dispute between them concerning the interpretation or application of this Treat though negotiations or other peaceful means of the Parties mutual choice.
- States Parties may pursue, by mutual consent, third party arbitration to settle any dispute between them, regarding issues concerning the implementation of this Treaty.
Article 23
Relations with States not party to this Treaty
- States Parties shall apply Articles 3-5 to all transfers of conventional arms within the scope of this Treaty to those not party to this Treaty.
Article 24
Relationship with other instruments
- States Parties shall have the right to enter into agreements on the trade in conventional arms with regards to the international trade in conventional arms, provided that those agreements are compatible with their obligations under this Treaty and do not undermine the objects and purposes of this Treaty.
Article 25
Depositary and Authentic Texts
- The Secretary-General of the United Nations is the Depositary of this Treaty.
- The original text of this Treaty, of which the Arabic, Chinese, English, Russian and Spanish texts are equally authentic.
DISHONEST HUMANITARIANISM? The invalid assumptions behind the United Nations’ small arms control initiatives
Thursday, June 14th, 2012DISHONEST HUMANITARIANISM? The invalid assumptions behind the United Nations’ small arms control initiative
By Jeff Moran
Next month diplomats from the world over will converge at the United Nations in New York to formally negotiate a legally binding Arms Trade Treaty (ATT). This is the culmination of over a decade of humanitarian advocacy and pre‐negotiations inside and outside the United Nations. It’s part of a larger global effort kick‐started in 2001 with the passage of a non‐legally binding resolution by the UN General Assembly. This resolution was called the “Programme of Action to Prevent, Combat and Eradicate the Illicit Trade in Small Arms and Light Weapons in All Its Aspects” (PoA).(1) This led to the creation of many initiatives, the most visible and contentious of which has been the ATT.
The ATT process formally got underway with two subsequent UN resolutions lead by the United Kingdom and is still Chaired by Argentine Ambassador Roberto Moritán. In 2006, the UN General Assembly adopted resolution 61/89 entitled “Towards an arms trade treaty: establishing common international standards for the import, export and transfer of conventional arms.”(2) This resolution enabled the UK and like‐minded countries to assemble experts to assess the feasibility of formally launching an ATT negotiation process. Then, in 2009, the UN General Assembly adopted resolution 64/48, entitled “The Arms Trade Treaty,” which established a schedule for pre‐negotiation meetings (known as Preparatory Committees, or PrepComs) resulting in a final Diplomatic Conference in July 2012.(3)
The goal of the ATT is to “to elaborate a legally binding instrument on the highest possible common international standards for the transfer of conventional arms.”(4) The scope is likely to include everything from helicopters to hand grenades, from tanks to target pistols and ammunition. It is hoped by humanitarians that a legally binding UN ATT championed by like‐minded states could be shaped to complement the merely politically‐binding 2001 UN PoA.
While all this treaty advocacy was going on, many of the same actors adopted a more discreet approach to binding international law for small arms and ammunition. Rather than just pursue their ambitious goals through a treaty out in the open, they also quietly started developing small arms control standards and customs. An example of this is the UN CASA (Coordinating Action on Small Arms) project, which is overseen by the UN’s Office of Disarmament Affairs.(5) UN CASA is euphemistically described as the “small arms coordination mechanism within the UN” to “frame the small arms issue in all its aspects, making use of development, crime, terrorism, human rights, gender, youth, health and humanitarian insights.”(6) In practice this organization is like a lawmaking committee or agency, but not nearly as accountable.
In 2008, CASA launched what they themselves described as “an ambitious initiative to develop a set of International Small Arms Control Standards (ISACS).”(7) UN CASA’s ISACS project includes eighteen mostly small and developing countries (none of them permanent security council members), fifteen international, regional and sub‐regional organizations, 33 humanitarian civil society groups, 23 other UN bodies, and just one Belgian firearms company, and one Italian national sporting arms and ammunition industry association.(8)
Ultimately, UN CASA’s ISACS initiative will eventually result in customary international law. Customary international law is the result of international administrative rule making which acquires the same weight as treaty law over time. States can be bound by customary international law regardless of whether the states have codified these laws domestically. Along with general principles of law and treaties, customary law is considered by the International Court of Justice, jurists, the United Nations, and its member states to be among the primary sources of international law.(9)
Truth be told, the UN’s PoA, the ATT, and CASA ISACS are predicated on false assumptions regarding small arms and ammunition. The two most important of which I will discuss here. Both of these assumptions are generally false in view of recent statistical studies and published scholarship.
The first assumption is that proliferation of small arms is a universal threat to human security, or, alternatively, that greater availability of small arms means more gun deaths in a given society. This is best quoted by the Geneva‐based Small Arms Survey (SAS), a special interest research group funded by various United Nations organizations, and other countries advocating stricter small arms controls.(10) The SAS officially states that the driving assumption behind all their research is the unqualified universal idea that “proliferation of small arms and light weapons represents a grave threat to human security.”(11) In fact, Nicholas Florquin, a senior researcher at SAS, started his talk during a two day seminar on Small Arms and Human Security in November 2011 with a stronger statement that, “proliferation of small arms causes problems” for humanity. (12)
Clearly, the small arms situation in some places may indeed be threatening to human security. But proliferation, i.e. the distribution of arms or expanding private ownership of arms, is not intrinsically a bad thing for everyone everywhere, especially in an ordered society. Proliferation, in fact, can be a force for good even in a disordered societal situation.
The American experience alone invalidates the global causative relationship between small arms proliferation and human insecurity. For example, trend data over the past nearly 20 years shows the US has been experiencing a phenomenal 35% decline in the number of gun deaths, even more in per‐capita terms.(13) This is part of a long term general trend in lower criminality. Over the same period firearms‐related suicides per 100,000 people declined by nearly 20%, the population grew over 20%, gun availability spiked (firearms sales boomed while statistically insignificant numbers of guns were bought back or otherwise destroyed), and, in 2011, indicators of national gun ownership rates increased to their highest level since 1993.(14,15) In other words, what we see in the US is the flipside of the assumption, that proliferation of small arms coincides with less gun violence. While this situation doesn’t necessarily mean more guns causes less gun violence, it does mean that the “more guns means more violence” assumption is simply not valid.
The French experience arming revolutionaries abroad invalidates the moral aspect of this first assumption, that proliferation is intrinsically bad. In fact, France alone has shown there can be a democratic and human rights upside of small arms proliferation. Have humanitarian campaigners forgotten that France armed liberty‐seeking American revolutionaries against colonial Britain? Are they denying that France also armed liberty‐seeking Libyan revolutionaries last year, and, ultimately, facilitated the demise of a regional dictator and notorious human rights abuser? These experiences prove even legally questionable state‐sponsored small arms proliferation to “insurgents” and “revolutionaries” can actually be a good thing for some societies and their local humanity.
The second assumption is that there is a plague of international illegal weapons trafficking threatening humanity everywhere. In fact, Rachel Stohl, the long‐time private consultant and insider working directly for Ambassador Moritán managing the ATT processes, has even published that “Without a doubt, it is the illegal arms trade and its various actors, agents, causes and consequences that capture our attention and motivate our action.”(16)
New research suggests the problem of illicit international trade in arms is not nearly as bad as first hypothesized over 10 years ago. Humanitarian campaigners’ evidence about the vast size, global scope, and cataclysmic impact of international illicit trafficking simply does not exist. Granted, it’s hard to quantify such illegal activity. Nontheless, the assertion that illicit international small arms trafficking is a major problem for the world has in fact been disproven over 10 years of progressively improved knowledge on the topic by academics and specialist researchers.(17)
To this day, however, the UN still claims on its Office of Disarmament Affairs website that international trafficking is a “worldwide scourge,” and that it “wreaks havoc everywhere.”(18) Campaigners, and their UN organizational sympathizers, must embrace the truth and acknowledge that the world is NOT actually suffering from a scourge of illegal international arms trafficking everywhere. At best, some failed or fragile states, conflict or post‐conflict regions may be suffering from illegal trafficking, but even this is of dubious importance ranked against other concerns like local diversion of small arms from government arsenals. Deaths and violence by small arms and light weapons are, on the whole, symptomatic of more local causes rooted within societies, and not cross‐border transfers.
The inconvenient truth today for humanitarian campaigners for international small arms controls is that for most countries around the globe, even for most developing or fragile states, a combination of deficient domestic regulation of legal firearms possession with theft, and loss or corrupt sale from official inventories is a more serious problem than illicit trafficking across borders.(19) The much touted scourge of illicit trade in small arms must be recognized, therefore, as hyperbolic humanitarian catastrophizing, or as we say in business, “marketing hype.”
In conclusion, while hyping of the size, scope, and impact of the illicit aspects of the arms trade was a de facto condition for first building consensus and momentum for the PoA, the ATT, and programs like CASA ISACS, continuing to do so presents serious reputational risk.(20) Continuing to assert that proliferation of small arms in society is intrinsically a bad thing for humanity presents serious reputational risk as well. Ultimately, such apparent dishonestly in the pursuit of otherwise admirable humanitarian goals raises questions about hidden agendas, institutional credibility, integrity, and organizational subject matter expertise. If the UN and humanitarian organizations really want to promote human security around the globe, honesty is still the best policy.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Jeff Moran, a Principal at TSM Worldwide LLC, is a business consultant specializing in the international defense & security industry. He studies negotiations & policy‐making at the Executive Masters Program of the Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies in Geneva, Switzerland. Previously Mr. Moran was a strategic marketing leader for a multi‐billion dollar unit of a public defense & aerospace company, a military diplomat, and a nationally ranked competitive rifle shooter. Jeff Moran has an MBA from Emory University’s Goizueta Business School and a BSFS degree from Georgetown University’s Walsh School of Foreign Service
© 2012. Jeff Moran and TSM Worldwide LLC. All Rights Reserved. Distribution and republication are authorized when Jeff Moran and URL are referenced. http://tsmworldwide.com/dishonest‐humanitarianism/ DISHONEST HUMANITARIANISM? The invalid assumptions behind the United Nations small arms control initiatives.
END NOTE
1 http://www.poa‐iss.org/PoA/poahtml.aspx
2 http://daccess‐dds‐ny.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N06/499/77/PDF/N0649977.pdf
3 http://daccess‐dds‐ny.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N09/464/71/PDF/N0946471.pdf
4 Ibid.
5 http://www.poa‐iss.org/CASA/CASA.aspx, http://www.un‐casa.org
6 http://www.poa‐iss.org/CASA/CASA.aspx
7 http://www.un‐casa‐isacs.org/isacs/Welcome.html
8 http://www.un‐casa‐isacs.org/isacs/Partners.html
9 http://www.ll.georgetown.edu/intl/imc/imcothersourcesguide.html, http://www.mpepil.com/sample_article?id=/epil/entries/law‐9780199231690‐e1393&recno=29&, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Customary_international_law
10 Small Arms Survey, established in 1999, is supported by the Swiss Federal Department of Foreign Affairs, and by sustained contributions from the Governments of Canada, Finland, Germany, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. The Survey is also grateful for past and current project support received from the Governments of Australia, Belgium, Denmark, France, New Zealand, Spain, and the United States, as well as from different United Nations agencies, programs, and institutes.
11 http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/about‐us/mission.html
12 November 4, 2011. This author was a note‐taker and participant in this seminar, which was hosted by the Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies.
13 http://bjs.ojp.usdoj.gov/content/homicide/tables/weaponstab.cfm, http://webappa.cdc.gov/sasweb/ncipc/mortrate10_us.html.
14 http://www.gallup.com/poll/150353/self‐reported‐gun‐ownership‐highest‐1993.aspx?version=print
15 http://webappa.cdc.gov/sasweb/ncipc/mortrate10_us.html
16 Rachel Stohl and Susan Grillot. The International Arms Trade. Polity Press: 2009. P. 93
17 Owen Greene and Nicholas Marsh, eds. Small Arms, Crime and Conflict: Global Governance and the Threat of Armed Violence. Routledge: 2012. P. 90.
18 http://www.un.org/News/Press/docs//2010/dc3247.doc.htm.
http://www.un.org/disarmament/convarms/SALW/
19 Owen Greene and Nicholas Marsh, eds. P. 91.
20 Anna Stavrianakis. Taking Aim At the Arms Trade: NGOs, global civil society, and the other world military order. Zed Publishing Ltd: 2010. P. 143‐4S

